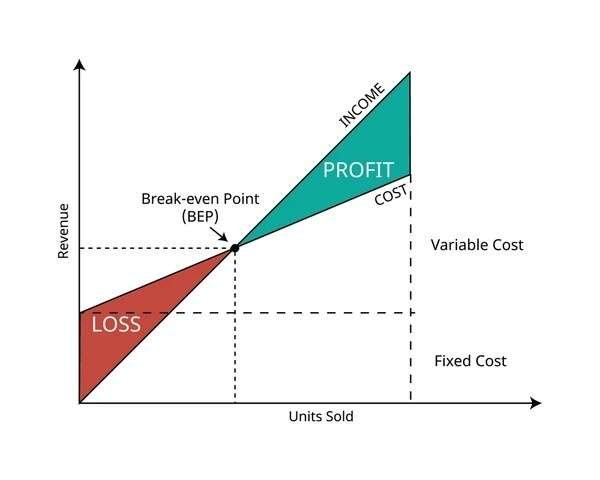
A breakeven chart is a graphical representation used in business and financial analysis to visually depict the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profits. It helps businesses understand at what point they will neither make a profit nor incur a loss.
Table of Contents
Definition and Purpose
Definition: A breakeven chart, also known as a breakeven analysis graph, illustrates the breakeven point by plotting total revenue, total costs, and the breakeven point on a graph.
Purpose: The primary purpose of a breakeven chart is to provide a clear visual representation of how changes in sales volume impact profitability. It helps businesses and financial analysts visualize the point at which revenue equals total costs, indicating a breakeven scenario.
Key Components and Construction
Components of a Breakeven Chart
- Sales Volume: Typically plotted on the horizontal axis (x-axis), representing the quantity of goods or services sold.
- Revenue and Costs: Plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis), representing monetary values.
Construction of a Breakeven Chart
- Fixed Costs: These are plotted as a horizontal line on the y-axis, indicating expenses that do not change with sales volume.
- Variable Costs: Represented as a slope from the origin (zero sales volume) upward, reflecting costs that increase with sales.
- Total Costs: The sum of fixed costs and variable costs, depicted as a line starting at fixed costs and sloping upward with sales volume.
- Total Revenue: Starts at zero sales and increases with sales volume, typically at a steeper slope than total costs.
- Breakeven Point: The point where the total revenue line intersects the total costs line, indicating the sales volume at which the business reaches breakeven.
Example Scenario
Consider a retail store selling handmade crafts:
- Fixed Costs: Rent and utilities totaling $2,000 per month.
- Variable Costs: Materials and labor costing $5 per unit.
- Selling Price: Each craft is sold for $20.
To construct a breakeven chart:
- Fixed costs of $2,000 are plotted as a horizontal line on the y-axis.
- Variable costs of $5 per unit are represented as a sloping line starting from zero units on the x-axis.
- Total costs (fixed + variable) form a line sloping upwards from $2,000, intersecting with the total revenue line.
Benefits and Applications
Benefits of Breakeven Charts
- Visual Clarity: Provides a clear visual representation of financial data, making it easier to interpret and analyze.
- Decision-Making: Facilitates informed decisions on pricing, production levels, and cost control measures.
Applications in Business
- Financial Planning: Helps businesses set achievable sales targets and forecast profitability.
- Performance Evaluation: Assists in evaluating the impact of changes in costs or pricing strategies on profitability.
Importance in Financial Analysis
Analytical Insights
- Profitability Assessment: Enables businesses to assess profitability at different sales volumes.
- Scenario Analysis: Allows for scenario planning based on varying levels of sales and costs.
Factors Affecting Breakeven Charts
Key Considerations
- Price Changes: Adjustments in selling prices affect the breakeven point and profitability.
- Cost Fluctuations: Variations in fixed and variable costs impact the slope and position of the total costs line.
Conclusion
A breakeven chart is a valuable tool in accounting and finance, providing a visual representation of the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profitability. By plotting fixed costs, variable costs, total costs, and total revenue, businesses can easily identify their breakeven point—the level of sales at which they cover all costs but make no profit. Understanding and utilizing breakeven charts help businesses make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, production levels, and cost management, ultimately contributing to financial stability and growth. Mastery of breakeven analysis and charts is essential for entrepreneurs, managers, and financial analysts seeking to optimize business performance and achieve sustainable profitability in competitive markets.