Crossing the Chasm refers to a critical stage in business growth where a new product transitions from early adopters to mainstream market acceptance. This article aims to explain Crossing the Chasm in simple terms, provide examples, and highlight its significance in business strategy.
Table of Contents
What is Crossing The Chasm?
Definition
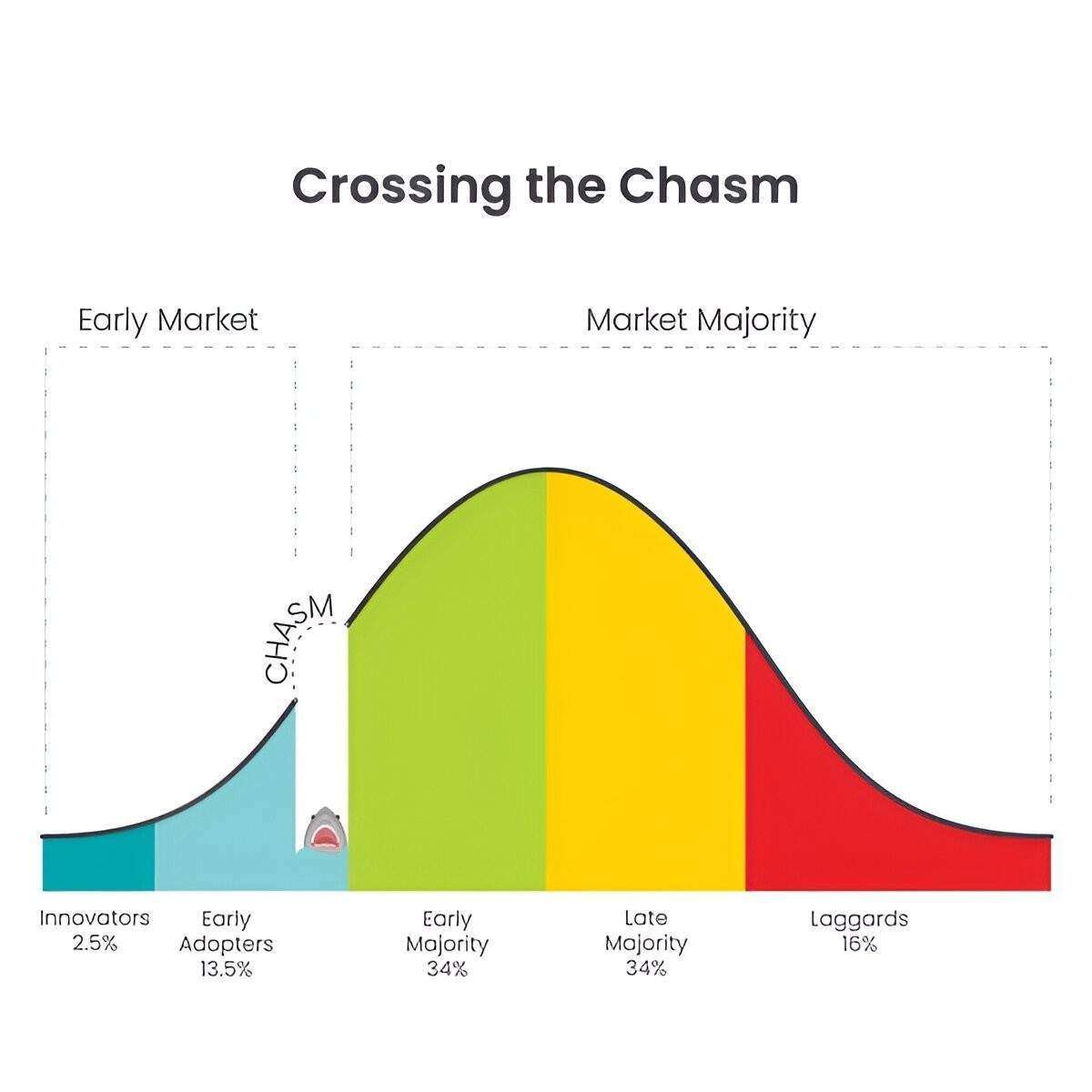
Crossing the Chasm is a concept introduced by Geoffrey Moore in his book “Crossing the Chasm: Marketing and Selling High-Tech Products to Mainstream Customers.” It represents the transition from gaining initial traction with early adopters to achieving widespread market adoption among mainstream customers.
Key Points
- Market Segmentation: Identifies different customer segments including innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards.
- Chasm: Represents the gap between early adopters (visionaries) and the early majority (pragmatists).
- Strategy Shift: Involves adapting marketing and sales strategies to appeal to the pragmatists who have different priorities and buying criteria.
Importance of Crossing The Chasm in Business
Market Expansion
Crossing the Chasm is crucial for scaling businesses beyond niche markets and establishing a broader customer base. It drives sustained growth by penetrating mainstream markets and gaining market share.
Revenue Growth
Successful crossing of the chasm leads to increased sales volumes and revenue streams as products gain broader market acceptance and adoption.
Competitive Advantage
Companies that effectively navigate the chasm gain a competitive edge by establishing market leadership and brand recognition among mainstream customers.
How Does Crossing The Chasm Work?
Example Scenario
Example: A startup develops a new mobile app targeting tech-savvy early adopters who value innovation and cutting-edge features. To cross the chasm, the company must modify its product and marketing strategy to appeal to mainstream users who prioritize usability, reliability, and customer support over advanced features.
Strategies for Crossing The Chasm
1. Targeting Early Majority
Strategy: Focus on the needs and preferences of the early majority (pragmatists) who seek proven solutions, references from peers, and tangible business benefits.
2. Product Positioning
Strategy: Position the product as a practical solution that addresses specific pain points of mainstream customers. Highlight reliability, ease of use, and customer success stories.
3. Marketing Messaging
Strategy: Tailor marketing messages to emphasize product benefits and ROI. Use case studies and testimonials to build credibility and demonstrate real-world value.
Challenges in Crossing The Chasm
Market Acceptance
Mainstream customers may be skeptical of new technologies or products without a proven track record or references from trusted sources.
Scalability
Scaling operations to meet increased demand and customer support requirements can strain resources and operational capabilities.
Ethical Considerations
Transparency and Integrity
Maintaining transparency in product capabilities and performance metrics is essential to build trust and credibility with mainstream customers.
Conclusion
Crossing the Chasm is a pivotal stage in the lifecycle of products and businesses, marking the transition from early adopters to mainstream market acceptance. By understanding customer segments, adapting strategies, and addressing specific market needs, businesses can successfully navigate the chasm and achieve sustainable growth. Effective marketing, product positioning, and customer engagement are key to crossing the chasm and establishing market leadership in competitive industries. As businesses innovate and expand into new markets, mastering the art of crossing the chasm remains essential for driving long-term success and achieving significant market impact.